Stanford University has convened the Ethics of Data conference this week bringing leaders from industry, humanitarian, research and civil society together to discuss and build plans for data ethics in all our work. I’m participating by co-leading a workshop on the redefining the Data Lifecycle with my colleague, Patrick Vinck of Harvard Humanitarian Initiative.
The Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team and the wider Crisismappers community are discussing and using drones and satellites to capture imagery of land changes, displaced camps and post-disaster areas. Some of the topics we are discussing within these communities include how to include local NGOs and the government. In times of crisis, humanitarians and technologists are moving very fast. We need to have more guidance, research and best practices. At the Ethics of Data event, we will use HOT as an example data project in our conversations.
The HOT community is incredibly committed to helping humanitarians and affected communities with maps. We are frequency discussing how and what types of aerial imagery be shared. What kind of training do we provide for review and use of aerial imagery? What happens to the data after the emergency? What kind of ethical code should we provide for all Digital Humanitarians? As HOT builds Open Aerial Map and groups like the UAViators come to existence, we need to consider data education and use beyond text and include video, photos and drone/satellite imagery. In the US, Mapbox is educating use of drones by creating a map of where not to fly. This work is moving faster than the research. It is my hope from the Ethics of Data event that I will be able to convene conversations within HOT to determine our next steps. Keeping in mind that every humanitarian situation is different as are the jurisdictions in which global, local and remote contributors participate.
What about the Data Pipeline?
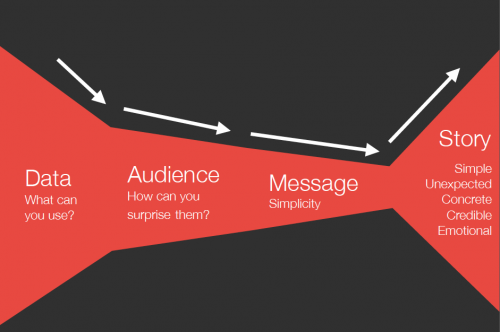
Data Storytelling via Infogr.am
All around the world journalists, civil society groups and governments are working on open data projects. HOT is just one of many projects aimed at using open data to affect change. Determining the new data pipeline could be informed by HOT’s experiences. In the past year, I have been at countless events where people talk about the importance of open data, the importance of the data pipeline and the impact of data storytelling. I also believe that data needs to be open, when appropriate. But, I am wary about preaching about open data without including a clear ethical compass. One of the main reasons that data is not open is that people do not trust how the data will be used. And, frankly, it is very unclear what constitutes a clean dataset. Over the past years, I have worked with Geeks without Bounds, Ushahidi and Data Science for Social Good to try and solve this challenge with checklists or tools. Every dataset begets new questions. All of our work needs to be infused with questions about data accuracy and data ethics. It is misplaced as an afterthought.
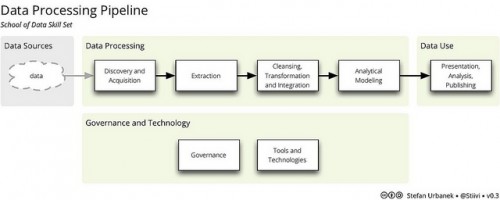
Processing the Data Pipeline
This is a Data pipeline via OKFN:
We need to create communities and tools with the data ethics checklists embedded into every aspect of projects from inception to funding to creation to education to analysis and to impact assessments. I’m truly looking forward to rethinking data project lifecycles and sharing the outputs with various communities to discover and remix together.
How would you rebuild the Data Lifecycle?
(Thanks to Nika Aleksejeva from Infogr.am for the Data Storytelling diagram.)