[Reposted from the Huffington Post, January 28, 2016]
It is now commonplace for people around the world to use social media during emergencies, and the volume of online information coupled with its rapid arrival is becoming increasingly overwhelming to humanitarian organizations. In response, digital humanitarians (individuals who participate in humanitarian relief online) have organized into skilled teams online to decipher the signals from the noise and thus provide accurate data. These teams work in partnership with formal humanitarian organizations using digital forensics, mapmaking, data mining, curation and open dialogue. Communication is now considered a crucial part of aid, and social media is part of this toolset. Even so, privacy, power and access are just some of the complex challenges that digital humanitarians must navigate when using these platforms in their work to help communities in need.
Introduction
Seeking a way to “do something,” more and more people are answering the call to action on social media after each emergency. Digital responders or “digital humanitarians” immediately log on when news breaks about a natural disaster or human-created catastrophe. Individuals and teams “activate” based on skill sets of volunteer and technical communities (VTCs). These digital responders use their time and technical skills, as well as their personal networks in an attempt to help mitigate information overload for formal humanitarian aid in the field. The terms often used to define these contributors in the humanitarian space are remote help, citizen engagement, citizen response, localized community, civil society and global civic technology. Some participants are new to online humanitarian response, but have found a topic or location that drives their passion to get involved.
This surge of action by participants is often just as chaotic as the actual physical emergency response. People are compelled to work, at a dizzying pace, by the fact that many parties involved in first response require valid, urgent and usable data. Focused on the needs of the citizens in affected areas, informal and formal networks collaborate and sometimes collide in an effort to make sense of and identify needs or stories from this user-generated content. With a combination of will and skill, they create updated maps, datasets, information products, and even communities (both online and offline). The global growth of these activities is based on access to information, connectivity and language skills as well as digital literacy levels. These groups are making efforts to become more inclusive while respecting local language, culture and knowledge. The mantra of most digital responders is “support” not “supplant” local citizens, humanitarians and emergency responders.
The role of digital communities in humanitarian response has been well documented in the past few years, from the UN Disaster 2.0 report to the rise of the CrisisMappers Network and beyond. A starting point might be the use of online bulletin boards (BBS) and mailing lists in response to the tsunami in Asia followed by a parallel timeline for most small and large humanitarian and conflict crises since 2004. The tools and volume have changed over time, but the propensity to connect and potentially help occurs after each incident. The fact is that every day there is a local or global emergency happening somewhere (slow onset or immediate), and there is a flood of online communications that follows immediately afterwards. The high volume of news and citizen data saturates online spaces with such speed that accurate reports and priority items can become a blur. This user-generated content (UGC) comes in many forms: texts, photos, aerial and satellite imagery, videos and more. Digital responders learn and refine techniques with each response.
Humanitarian organizations and the citizens they serve are overwhelmed by the speed of change and the onslaught of information. In the five years since the Haiti earthquake, there has been a steady progression of change. Humanitarian groups have sometimes resisted incorporating social media into their information workflows. Often this is due to process changes, a lack of trust, concerns about accuracy and fear of change. People who create user-generated content are often considered outliers and have not yet gained the trust of leaders within official institutions. And having people in affected regions use these tools to help each other or ask for help changes the information flow from one-way to two-way. Humanitarian institutions simply adapt to change at a slower pace. They also have a low capacity to review information outputs and seldom have the funds to incorporate UGC into their processes. Plus, they often do not understand the tools and techniques these online/offline communities use to connect. The conundrum is that UGC and citizens are simply changing faster. As a result, this gap between the two groups is being tested and often fulfilled in new ways.
Across the world there are branded hubs, labs, fellowships, meetings, conferences and research. Governments, international non-governmental organizations (INGOs) and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are all working on various projects. How can these new voices and communities become part of the humanitarian apparatus? From Unicef Innovation to Ihub Nairobi, Kathmandu Living Labs to UN Global Pulse Jakarta, there are many new spaces where solutions have been observed and created. There is a parallel stream with groups like the Code for All community and other civic technology or humanitarian technology/research communities who aim to connect software developers, data scientists and designers to solve hyperlocal issues with official organizations. Code for All has grown from its base in the United States to Japan and beyond. Their goal is to connect local communities and governments with digital technologies and problem solvers for all issues. The intersection of these two movements is inevitable in risk-prone areas.
Digital Response Communities, Their Scope and Effectiveness
The Digital Humanitarian Network consists of many groups, from those that create maps, like Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team, and those who curate social information like Humanity Road and Standby Task Force, to those bridging language skills like Translators without Borders. Digital responders coalesce during an emergency to tackle tasks that can be large or small. For instance, over 2,800 people contributed to the Nepal earthquake response by doing small tasks such as using MicroMappers to make quick decisions about text or images. These curated information insights were used by over 250 organizations to make decisions about various needs for their response, including damage assessments and aid distribution. This example shows that UGC can be created by anyone, but someone still needs to parse the data, find the crucial points and match these items to needs and actions. After reviewing the IP addresses of contributors, Qatar Computing Research Institute observed that the majority of these digital MicroMapper helpers were from northern countries.
For the Nepal earthquake response, over 7,500 people contributed to improve OpenStreetMap in a short span of time. OpenStreetMap is the Wikipedia of maps, creating a large free and open dataset that anyone can use. The Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (a VTC) creates tools and training to support mapping for humanitarian response and economic development. The Nepal Earthquake response was co-lead by the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team and Kathmandu Living Labs. Kathmandu Living Labs, started in 2013, creates local data and map solutions and partnerships for Nepal. They have steadily built a local community of mappers trained to use OpenStreetMap, and they have mapped the country. Over the years, they have also built relationships with a range of local partners, from emergency responders to universities. When the Nepal earthquake struck, they lost their office and a day’s worth of work. Meanwhile, remote digital responders in the Humanitarian OpenStreetMap Team (HOT) community activated. HOT, with the generous support of partners, obtained both pre- and post-disaster satellite imagery to determine the regions of Nepal that might be affected.
While they are informal, these networks are all driven by the common vision of UGC for humanitarian response. Simply put, they move fast and have the initiative to do what is most needful. For example, the OpenStreetMap Japan Foundation community translated the Guide to Mapping Buildings in Nepal from the Kathmandu Living Labs. Thus one former disaster-affected civic technology community activated to aid another, transferring skills and supporting digital needs. No government or formal institution advised that this was required; people simply self-organized based on digital responder knowledge and the desire to help their digital neighbours. While these processes are not yet seamless, the gap between official and informal is closing with each response.
Three Challenges
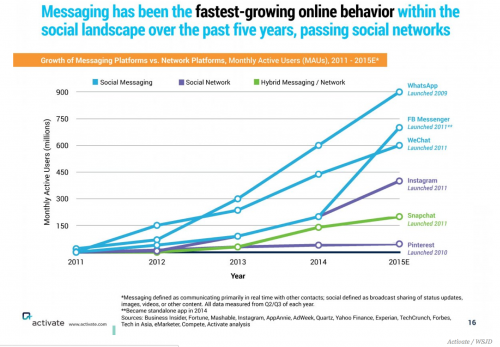
1. At the moment, the vast majority of social media is available via public posts. But with huge growth in private messaging tools like WhatsApp, how will digital response incorporate data from platforms like this?
2. In times of crisis, data becomes the lifeblood of managing humanitarian operations. But as access to data increases, how will people safeguard the privacy and security of those who need help?
3. What role should the main social platforms play during disasters? Can these social networks work together more closely to coordinate their responses?
This post is part of a series produced by The Huffington Post and The World Economic Forum sharing insights gained from surveying 5,000 digital media users from Brazil, China, Germany, South Africa and the U.S on the impact of digital media on society. The series is developed in conjunction with the Forum’s Shaping the Future Implications of Digital Media for Society project and the Forum’s Impact of Digital Content: Opportunities and Risks of Creating and Sharing Information Online white paper. The series is running during the Forum’s Annual Meeting 2016 (in Davos-Klosters, Switzerland, Jan. 20-23). Read all the posts in the series here.