We are neighbours, no matter where we live. Being a new resident to Doha, I am grappling with a number of questions. These stem from working with humanitarian and crisis information for a number of years. Plus, it is part of my mandate at Qatar Computing Research Institute to help apply research and software to support local needs. We have learned much globally about emergencies. I’d like to learn more about how to help locally and who is keen to collaborate.
How will Doha and Qatar prepare for the upcoming information overload? What are the communications plans during an emergency? How will the public use or not use social media or new technology during an emergency? What are the information and technology needs in the GCC (Gulf Cooperation Council)? How does preparedness compare to other regions? How can citizens and communities prepare? How can Digital Humanitarians be of service? How would Digital Humanitarian community in Qatar differ? What are the training and technology needs of digital humanitarians locally? How can the local Digital Humanitarian community get more involved in the global community? How would Qatar Computing Research Institute’s work apply or not apply for emergencies in the region? What other types of research and/or software would serve the local responders and communities?
In September I attended the GCC Government Social Media Summit in Dubai. There were a number of presentations about preparedness and communications. I was interested to learn that in Dubai, every neighbourhood has a #hashtag. It is used for community activities but my colleague Ali Rebaie advised that this practice is also used for emergencies or resilience. This is something that happens around the world. Neighbours online are networks and information ambassadors locally (offline). This is invaluable. How can we apply this to Doha? Maybe because we are a smaller city and country, we organize primarily around #Doha or #Qatar. There should be tags for all social media platforms in multiple languages by districts and cities. By doing this, we can plan and share for communications.
The Qatar Red Crescent Disaster Management Camp in April 2015 provided great insights into how communication flows among responders. My observations found that people use WhatsApp to organize but are keen to investigate how social media might also be a communications channel. This participation has provided an impetus and goal to host a local social media and emergency meetups. Bringing responders and local enterpreneurs into the same space has started with the joint QCRI and Qatar Red Crescent Digital Humanitarian workshops. But, we do need to talk more about how social media will or won’t be a factor in Doha. How will people communicate during an emergency? How will responders work with them? At minimum, there needs to be local ‘information ambassador’ programme setup on WhatsApp. The more training the more ready we are for emergencies. The Qatar Red Crescent has been doing preparedness and resilience training in communities and with schools. Businesses may be thinking about text messages (SMS) during emergencies. But as a new resident working in these spaces, I do see opportunities to help.
Civil Defense Exhibition and Conference is hosting preworkshops on preparedness, community risk reduction, evacuation and infrastructure planning. All week for 5 hours a night I have joined about 60 people to learn from experts in the field. Participants are from across emergency response, civil defense, business and research. Questions have been fascinating. The earnestness to plan for all the stakeholders is very evident. While the mandate was not about ‘how communities will communicate’, it is very much on the minds of organizers and participants. All of this highlights the need for a more research on how will responders and communities work together.
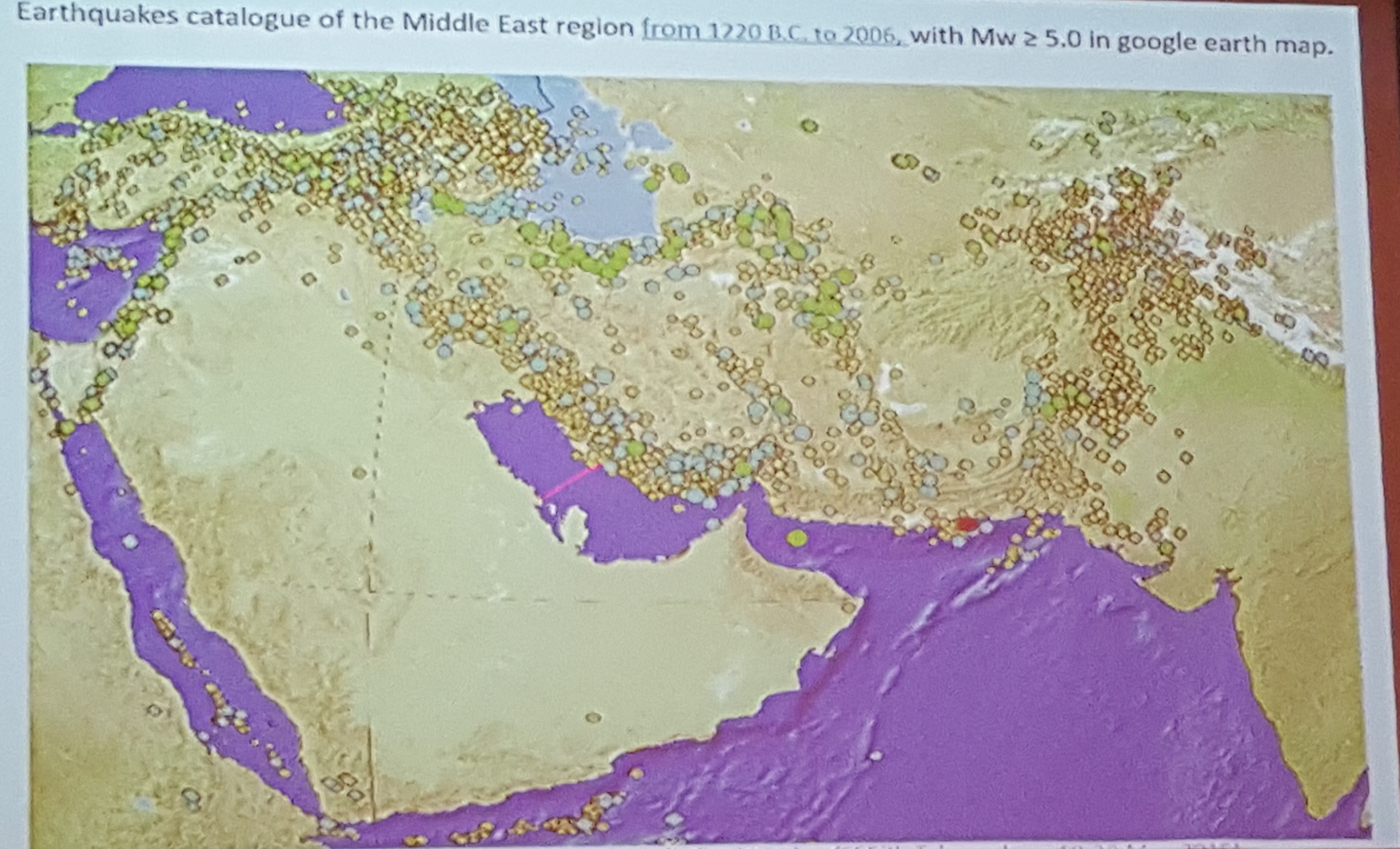
(Map presented by the Professor Zare of the International Institute of Earthquake Engineering and Seismology, IIEES (Tehran, Iran))
There is a large multilingual and high-volume mobile telephone penetration. I’ve found some success in building informal alliances and finding allies. In talking with many stakeholders, there is an enthusiasm to build more plans around communications and citizen engagement for preparedness. Who should I talk with who is interested in communications and emergencies in Doha, Qatar or the GCC?